Charge Beyond Boundaries – What is EV Roaming?
Imagine you're on a road trip with your electric vehicle (EV), and you need to charge it along the way. Normally, you use a specific app to find charging stations near you, but what if you're in a new city or area? That's where "roaming" comes in. Just like using your phone in a different network when you travel, roaming in EV charging lets you use charging stations from different networks, even if they're not part of your usual network.
However, just like phone roaming, it might cost a bit more depending on the network or location. Some networks work together seamlessly, so you can charge without setting up multiple accounts, but you might pay extra for the convenience.
Understanding the Difference Between Peer-to-Peer Roaming and Roaming Hub in EV Charging
When it comes to EV charging, both Peer-to-Peer Roaming and Roaming Hubs make it easier for drivers to charge their vehicles across different networks. However, the way they work is quite different, and it's important to understand these differences.
Peer-to-Peer Roaming
Peer-to-peer roaming is like creating individual friendships between two charging networks. Each network has to establish a direct connection with every other network it wants to collaborate with. These are called bilateral agreements.
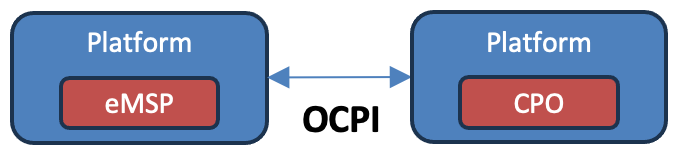
- How It Works: If your favorite mobile app (e.g., MApp1) wants to give you access to chargers from another app (e.g., MApp2), the two networks need to integrate directly. For every new network MApp1 wants to add, it has to go through a separate integration process.
- Example: Let’s say MApp1 has 100 chargers in Chennai, and MApp2 has 200 chargers in Bangalore. To give you access to all 300 chargers, MApp1 and MApp2 must set up a direct agreement. If MApp1 wants access to a third network (e.g., MApp3), another integration is required.
Key Challenge: This approach can be time-consuming and costly because every new partnership requires separate negotiations and technical work.
Roaming Hub
A roaming hub works like a central marketplace or a "one-stop shop" that connects multiple networks in one place. Instead of integrating with each network individually, your app only needs to connect with the hub once.
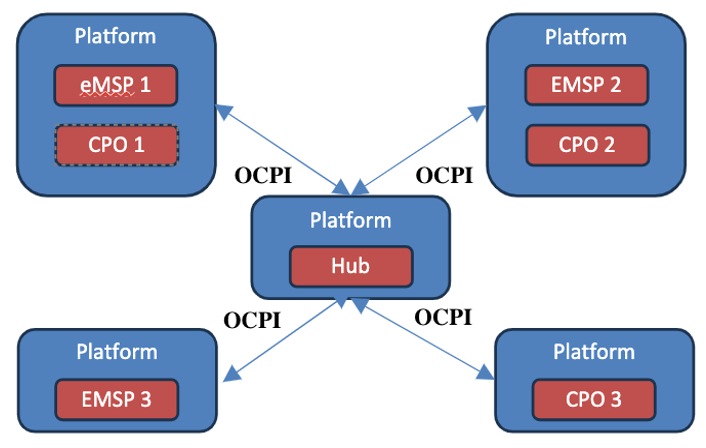
- How It Works: Your favorite app (e.g., MApp1) integrates with the roaming hub. Once connected, any other network that joins the hub automatically becomes accessible through MApp1 without additional integrations.
- Example: If MApp1 connects to a roaming hub, and this hub already includes networks like MApp2, MApp3, and others, you instantly gain access to all their chargers. Even if new networks join the hub later, you don’t need additional integrations-MApp1 will automatically extend access.
Key Advantage: A single integration with the hub simplifies everything, saving time and effort while giving you access to a much larger pool of chargers.
In summary:
- Peer-to-peer roaming is suitable for small-scale collaborations but becomes complex as more networks are added.
- Roaming hubs are ideal for large-scale interoperability, providing broader coverage with minimal effort.
by Sadguna Manubrahma
Product Manager - Roaming & Data Products
TruePower by JioThings