Accelerating the Shift: A Global vs Indian Perspective on EV Policies and Incentives
India is pioneering alternative pathways to electrification that may eventually influence mobility solutions worldwide, particularly in other developing economies.

How do global EV policies, regulations, and incentives support the development of the ecosystem, and how are Indian policies, regulations, and incentives supporting EVs and their ecosystem?
Outset
Electric car markets are seeing an exponential growth as sales exceeded 10 million in 2022. A total of 14% of all new cars sold were electrified in 2022, up from around 9% in 2021 and less than 5% in 2020.
China was again the frontrunner, accounting for around 60% of global electric car sales. More than half of the electric cars on roads worldwide are now in China and the country has already exceeded its 2025 target for new energy vehicle sales. In Europe, the second largest market, electric car sales increased by over 15% in 2022, meaning that more than one in every five cars sold was electric. Electric car sales in the United States – the third largest market – increased 55% in 2022, reaching a sales share of 8%.
There are promising signs for emerging electric vehicle (EV) markets, albeit from a small base. Electric car sales are generally low outside the major markets, but 2022 was a growth year in India, Thailand and Indonesia. Collectively, sales of electric cars in these countries more than tripled compared to 2021, reaching 80 000. For Thailand, the share of electric cars in total sales came in at slightly over 3% in 2022, while both India and Indonesia averaged around 1.5% last year.
Introduction
The global electric vehicle (EV) market has experienced unprecedented growth over the past decade, transforming from a niche segment to a mainstream automotive revolution. While countries like Norway, China, and the United States have made significant strides in EV adoption, India has been charting its own unique path. This article examines the contrasting landscapes of global EV developments and India's emerging EV ecosystem, highlighting the challenges, opportunities, and distinctive approaches that characterize each market.
Global EV Market: Rapid Growth and Transformation
Market Leaders and Their Approaches
China has emerged as the world's largest EV market, accounting for approximately 60% of global EV sales. The Chinese government's aggressive policies, including substantial subsidies, manufacturing incentives, and strict emission regulations, have created a thriving ecosystem. Companies like BYD, NIO, and SAIC have become global players, with BYD even surpassing Tesla in total EV sales in 2023.
Europe has seen remarkable growth, particularly in Norway where EVs now represent over 80% of new car sales. The European Union's stringent CO2 emission standards for automakers have accelerated electrification across the continent, with countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands offering significant tax incentives and infrastructure investments.
The United States has experienced a resurgence in EV adoption, driven by Tesla's success and more recently by policy initiatives including the Inflation Reduction Act, which provides substantial manufacturing incentives and consumer tax credits for domestically produced EVs.
Key Success Factors in Global Markets
Several factors have contributed to successful EV adoption in leading markets:
- Robust Policy Support: Long-term, consistent policy frameworks including purchase incentives, manufacturing subsidies, and emissions regulations
- Extensive Charging Infrastructure: Dense networks of public charging stations, including high-speed charging along highways
- Diverse Vehicle Options: Wide range of EV models across various price segments
- Battery Technology Advancements: Significant improvements in battery density, charging speeds, and cost reduction
- Local Manufacturing Ecosystems: Development of complete supply chains including battery production
India's EV Journey: A Unique Path Forward
Current State of India's EV Market
India's EV market, while growing rapidly, represents a smaller portion of total vehicle sales compared to global leaders. As of 2023, EVs constituted approximately 5% of total vehicle sales in India, with two and three-wheelers dominating the electric segment rather than passenger cars.
India's Distinctive Approach
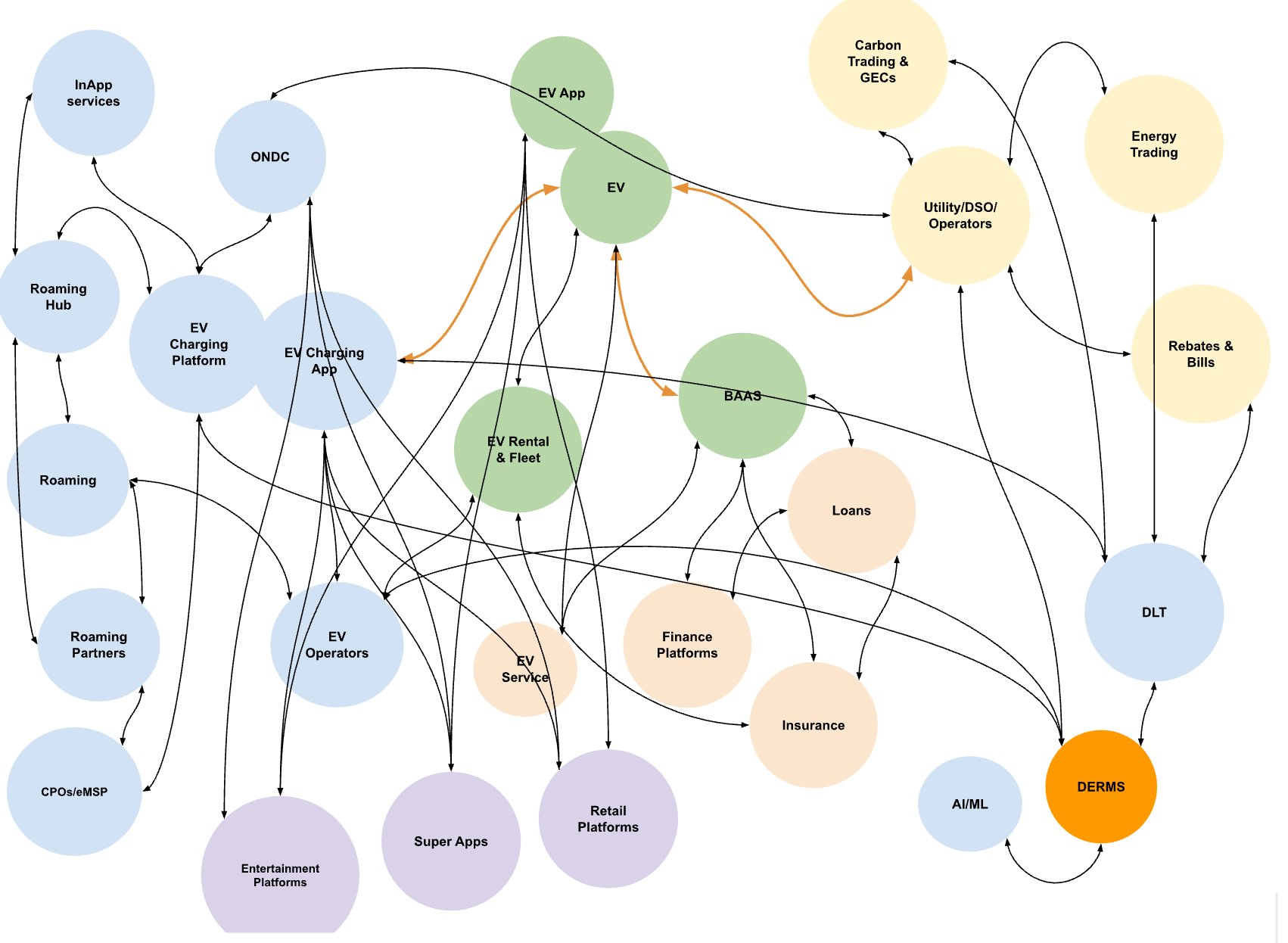
Two and Three-Wheeler Focus: Unlike global markets where passenger cars lead electrification, India has prioritized two and three-wheelers – segments that represent the largest portion of India's vehicle fleet and are more cost-sensitive to fuel savings.
FAME Scheme: The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme has provided subsidies primarily targeting public and shared transportation, commercial vehicles, and smaller personal vehicles.
Battery Swapping Infrastructure: Rather than focusing exclusively on charging infrastructure, India has embraced battery swapping technology, particularly for commercial vehicles and two-wheelers, addressing range anxiety and reducing upfront costs.
PLI Scheme: The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme aims to build domestic manufacturing capabilities across the EV value chain, reducing dependence on imports.
Challenges Specific to India
- Price Sensitivity: The Indian consumer market is extremely price-sensitive, making the higher upfront cost of EVs a significant barrier
- Infrastructure Limitations: Inadequate power grid capacity in many areas and limited space for home charging in dense urban environments
- Range Requirements: Long-distance travel needs in a geographically vast country with varying climate conditions
- Supply Chain Dependencies: Reliance on imported battery cells and electronic components
- Financing Challenges: Limited financing options and higher interest rates for EV purchases compared to conventional vehicles
Comparative Analysis: Key Differences
Policy Approaches
Global Markets: Aggressive emissions regulations forcing automakers to accelerate EV production; substantial consumer incentives for passenger vehicles
India: Targeted approach focusing on commercial vehicles and smaller personal mobility solutions; emphasis on domestic manufacturing through PLI schemes
Vehicle Segments
Global Markets: Passenger cars constitute the primary EV segment with SUVs increasingly dominant
India: Two and three-wheelers lead electrification efforts, with electric buses gaining traction in public transportation
Infrastructure Development
Global Markets: Extensive DC fast-charging networks along highways enabling long-distance travel
India: Battery swapping networks complementing traditional charging infrastructure, particularly for commercial applications
Market Dynamics
Global Markets: Established automotive giants competing with EV-native companies like Tesla
India: New entrants like Ola Electric disrupting traditional automotive hierarchies, particularly in two-wheeler segment
Future Outlook and Convergence
Despite these differences, several trends suggest potential convergence:
- Localization of Supply Chains: Both global markets and India are prioritizing domestic manufacturing of EVs and components
- Renewable Energy Integration: Growing focus on pairing EV charging with renewable energy sources
- Vehicle-to-Grid Applications: Exploring bidirectional charging capabilities to support grid stability
- Software-Defined Vehicles: Emphasis on connectivity and over-the-air updates across all markets
- Shared Mobility Electrification: Ride-sharing and fleet operators leading commercial applications
Conclusion
While global EV markets have demonstrated the viability of large-scale electrification, India's unique approach reflects the specific needs, constraints, and opportunities of its transportation ecosystem. Rather than simply following the global template, India is pioneering alternative pathways to electrification that may eventually influence mobility solutions worldwide, particularly in other developing economies.
The contrasting journeys highlight that EV adoption is not a one-size-fits-all proposition. Success requires tailoring approaches to local economic conditions, consumer preferences, and infrastructure realities. As both global markets and India continue to innovate in the EV space, cross-pollination of ideas and technologies will likely accelerate the global transition to sustainable mobility.
References:
https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2023/executive-summary#abstract
https://www.trade.gov/market-intelligence/germany-electric-vehicles-and-charging-infrastructure
https://alternative-fuels-observatory.ec.europa.eu/transport-mode/road/germany
-Balakumar
VP-Engineering